1.1 Location
India - an ancient civilisations in the world.
- After Indepedence (five decades) it has gone thorugh socio-economic development.
Various fields India has progressed in - Agriculture, Industry, Technology, and overall economic development.
India - vast country
India lies entirely in northern hemisphere. We can say that it lies in the North-East (NE) quadrant of the globe as shown in the figure 1.1.1 below.
![Solved] In which hemisphere does India lie?](https://storage.googleapis.com/tb-img/production/20/07/89965-004-105FBFAB.gif)
Figure 1.1.1 India's location on the globe
Mainland - land relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it.
Island - piece of land surrounded by water on all sides.
Pennisula - piece of land surrounded by water on only three sides.
Equator - an imaginary line around the middle of the Earth. It is halfway between the North and South Poles, and divides the Earth into two equal parts, the Northern and Southern Hemisphere
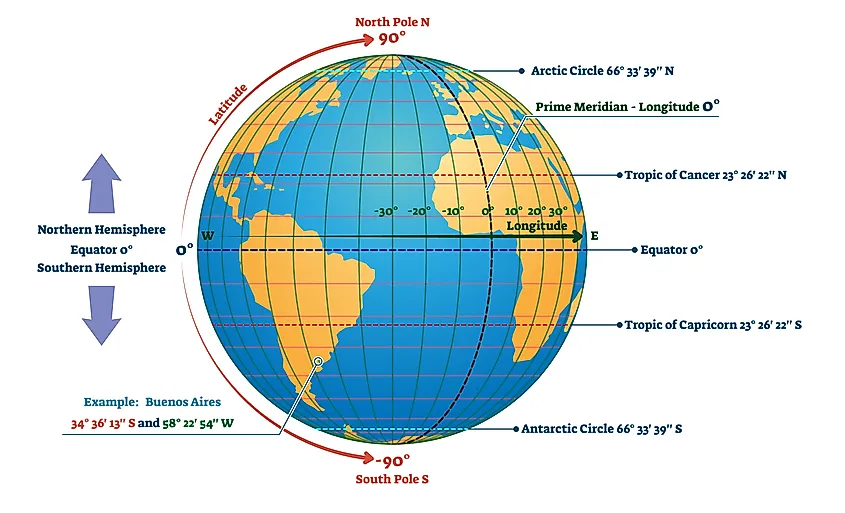
Figure 1.1.2 Equator, Prime (Greenwich) Meridian Line, Latitudes, Longitudes
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°.
Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great circle.
This great circle divides a spheroid, like the Earth, into two hemispheres: the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere (for an east-west notational system).
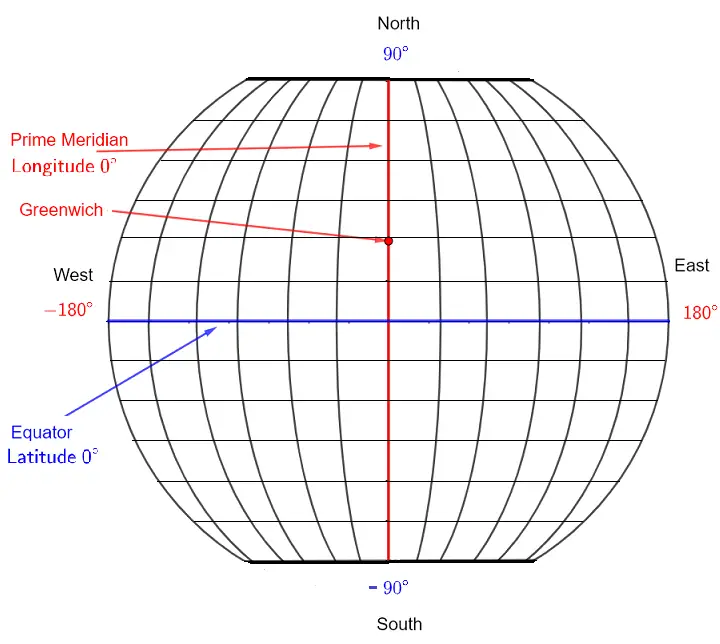 Figure - 1.1.3 Equator and Prime Meridian
Figure - 1.1.3 Equator and Prime Meridian
Latitudes and Longitudes are angular measurements that give a location on the earth’s surface a unique geographical identification.
Latitudes - Lines of latitude, also called parallels, are imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run east to west, but measure your angular position north or south. The equator is the most well known parallel. At 0 degrees latitude, it equally divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. From the equator, latitude increases as you travel north or south, reaching 90 degrees at each pole. As shown in Figure below :-
Latitudes are the progressive angular measurements north or south of the equator are the imaginary lines running from east to west on the Earth’s surface.
Figure - 1.1.4 Latitudes and major parallels of latitudes.
Latitude is the measurement of distance north or south of the Equator.
It is measured with 180 imaginary lines that form circles around Earth east-west, parallel to the Equator.
These lines are known as parallels. A circle of latitude is an imaginary ring linking all points sharing a parallel.
The Equator is the line of 0 degrees latitude. Each parallel measures one degree north or south of the Equator, with 90 degrees north of the Equator and 90 degrees south of the Equator.
The latitude of the North Pole is 90 degrees N, and the latitude of the South Pole is 90 degrees S.
Longitudes - While Longitudes are the measurements east or west of the Prime Meridian and run from the north pole to the south pole. As shown in figure below -
Note: - Latitudes are parallel while Longitudes are convergent.
This positioning method comprises of a coordinate system in degrees (°) with the Equator and Prime Meridian being the lines that denote 0°.
With the Equator as the reference point, the North Pole lies at 90°N and the South Pole lies at 90°S.
Likewise, the furthest point eastwards from the Prime Meridian is expressed as 180°E and the furthest point westward is expressed as 180°W.
Circles of Latitude are imaginary east to west circles that connect all places with the same latitude.
The reference plane for all Circles of Latitude is the Equatorial Circle of Latitude that bisects the Earth.
All Circles of Latitude are parallel to the Equator and perpendicular to all Longitudes at the intersection points.
Parallels get smaller towards the poles than closer to the Equatorial Plane.
Unlike latitudes that have the Equator as the central Latitude, the Prime Meridian has been set as the reference point of meridians over the course of history.
Circles of Latitude are called parallels while half of a longitudinal circle is called a Meridian. Meridians are important for setting time zones.
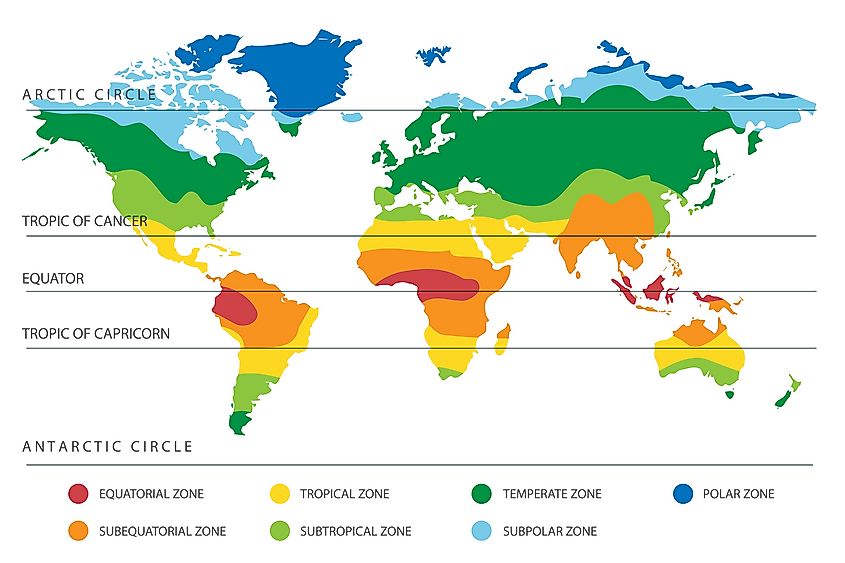
There are five main parallels that are useful to explain the correlation between the Earth, the Sun, and climate. As such, these five main parallels also mark the five geographical zones. These are:
Arctic Circle: It is the boundary of the North Frigid Zone to the north.
Tropic of Cancer: It encloses the North Temperate Zone with the Arctic Circle.
The Equator: It divides the earth in North and Southern Hemispheres . The area around the Equator is referred to as the Tropics and is limited northward by the Tropic of Cancer and southward by the Tropic of Capricorn.
Tropic of Capricorn: Encloses the South Temperate Zone with the Antarctic Circle.
Antarctic Circle: Is the boundary of the South Frigid Zone to the south.

Arctic Circle -
The Arctic Circle parallel that is currently positioned at 66° 33’ 46” in the Northern Hemisphere ( or 66.5628°).
The position of the Arctic Circle fluctuates by about 49 ft each year due to the Earth’s axial tilt that is determined by tidal forces resulting from the pull of the moon on the Earth’s waters.
The fluctuation of the Arctic Circle has been found to be at a rate of 2° every 40,000 years. The region north of the Arctic Circle called the North Frigid Zone is characterized by extremely cold temperatures and ice.
During the winter, the region experiences 24 hours of darkness in a day and 24 hours of sunlight in a day during the summers.
Antarctic Circle
This parallel of latitude is currently at 66° 33′ 46″ south of the Equator (or -66.5628°).
Like the Arctic, the position of the Antarctic Circles is not fixed, as their exact location depends on the Earth's axial tilt, which fluctuates within a margin of 2° over a 40,000 year period, mainly due to tidal forces resulting from the orbit of the Moon.
The Tropic Of Cancer
Tropic of Cancer is a Circle of Latitude currently positioned at 23°26’14” north of the Equator (or 23.4372°).
Another reference for the Tropic of Cancer is the Northern Tropic.
The Northern Tropic is the parallel at which the Summer (or Nothern or June) Solstice occurs when once a year the sun appears directly overhead the most northerly parallel.
This event happens in the month of June.
The Tropic Of Capricorn
Tropic of Capricorn is another Circle of Latitude currently positioned at 23°26’14” south of the Equator (or -23.4372°).
The Southern Tropic is another reference for the Tropic of Capricorn.
The Tropic of Capricorn is the parallel at which the Winter (or Southern or December) Solstice occurs when once a year the sun appears directly overhead the most southerly parallel.
This event happens in the month of December.
These two parallels enclose the area of the Earth known as The Tropics characterized by warm to hot weather and lush vegetation.
Similar to the Arctic Circle, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn also fluctuate depending on the Earth’s axial tilt.
The Equator
The Equator is the parallel line located at 0°00’00”.
It is identified as the latitude that falls at the point that is equidistant from the North Pole and the South Pole.
The Equator’s covers a distance on the Earth’s surface approximately 24,901 miles long.
The sun is perpendicular to the Equator twice a year in March and September. This event is called the Equinox.
Areas on the Earth’s surface that fall on the Equator’s path are characterized by almost constant lengths of day and night.
Likewise, the Equator fluctuates and is identified as the plane that is perpendicular to the Earth’s rotational axis.
Prime Meridian

The Prime Meridian is the meridian defined as 0°00’00” longitude.
It is the longitudinal meridian of reference.
Unlike the Equator’s position that is determined by the Earth’s rotational axis, the position of the Prime Meridian has been defined arbitrarily over the years as Greenwich in the United Kingdom.
The Prime Meridian divides the earth into two hemispheres, the Western Hemisphere to the west and the Eastern Hemisphere to the east.
The Tropic of Cancer, for instance, is 23 degrees 26 minutes 21 seconds N—23° 26' 21'' N. Its twin, the Tropic of Capricorn, is 23° 26' 21'' S. The tropics are important geographic locations that mark the northernmost and southernmost latitudes where the sun can be seen directly overhead during a solstice.
One degree of latitude, called an arc degree, covers about 111 kilometers (69 miles). Because of Earth's curvature, the farther the circles are from the Equator, the smaller they are. At the North and South Poles, arc degrees are simply points.
Degrees of latitude are divided into 60 minutes. To be even more precise, those minutes are divided into 60 seconds. One minute of latitude covers about 1.8 kilometers (1.1 miles) and one second of latitude covers about 32 meters (105 feet).
For example, the latitude for Cairo, Egypt, in degrees and minutes would be written as 29° 52' N, because the city is 29 degrees, 52 minutes north of the Equator. The latitude for Cape Town, South Africa, would be 33° 56' S, because the city is 33 degrees, 56 minutes south of the Equator. Using seconds of latitude, global positioning system (GPS) devices can pinpoint schools, houses, even rooms in either of these towns.
Similar to latitude, the corresponding measurement of distance around the Earth is called longitude. The imaginary lines of latitude and longitude intersect each other, forming a grid that covers Earth. The points of latitude and longitude are called coordinates, and can be used together to locate any point on Earth.
FAST FACT
54-40 or Fight!
An area of the circle of latitude at 54 40' N was a hotly contested piece of real estate in the 19th century. The U.S. and the United Kingdom (Canada) both asserted claims to the Pacific Northwest, in what became known as the Oregon Boundary Dispute. "54-40 or fight!" was a cry of American settlers. The boundary between the U.S. and Canada was eventually established at the 49th parallel.
An equator is an imaginary line around the middle of a planet or other celestial body. It is halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole, at 0 degrees latitude. An equator divides the planet into a Northern Hemisphere and a Southern Hemisphere.
The Earth is widest at its Equator. The distance around the Earth at the Equator, its circumference, is 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
The Earth's diameter is also wider at the Equator, creating a phenomenon called an equatorial bulge. The diameter of a circle is measured by a straight line that passes through the center of the circle and has its endpoints on the boundary of that circle. Scientists can calculate the diameter of latitudes, such as the Equator and Arctic Circle.
The Earth's diameter at the Equator is about 12,756 kilometers (7,926 miles). At the poles, the diameter is about 12,714 kilometers (7,900 miles). The Earth's equatorial bulge is about 43 kilometers (27 miles).
The equatorial bulge means that people standing at sea level near the poles are closer to the center of the Earth than people standing at sea level near the Equator. The equatorial bulge affects the ocean, too—sea levels are slightly higher in equatorial regions than near the poles.
The equatorial bulge is created by the Earth's rotation. As lines of latitude increase in size, a point has to travel faster to complete a circle (revolution) in the same amount of time. The rotational speed, or spin, at the Arctic Circle is slower than the spin at the Tropic of Cancer, because the circumference of the Arctic Circle is much smaller and a point doesn't have to travel as far to complete a revolution. The spin at the Tropic of Cancer is much slower than the spin at the Equator. Near the poles, the Earth's rotational speed, or spin, is near zero. At the Equator, the spin is about 1,670 kilometers per hour (1,038 miles per hour).
The Earth's gravitational pull is slightly weaker at the Equator due to its equatorial bulge.
The slightly weaker gravitational pull and momentum of the spinning Earth makes equatorial regions ideal places for space launches. It takes an enormous amount of energy to launch a satellite or other spacecraft out of the Earth's atmosphere. It takes less energy (rocket fuel) to launch in lower gravity. It also takes less energy to launch when the spinning Earth is already giving the satellite a push of 1,670 kilometers per hour (1,038 miles per hour).
The United States launches most spacecraft from the Kennedy Space Center in southern Florida, as close to the Equator as possible in the continental U.S. Other rocket-launching facilities near the Equator include Shaba North, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Gan Island, Maldives.
Recently, mobile launch platforms, such as Ocean Odyssey, have successfully launched satellites into orbit from the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
Equatorial Climates
Twice a year, during the spring and autumn equinoxes, the sun passes directly over the Equator. Even during the rest of the year, equatorial regions often experience a hot climate with little seasonal variation.
As a result, many equatorial cultures recognize two seasons—wet and dry. The wet, or rainy, season often lasts most of the year. The long, warm, rainy season creates tropical rain forests. Some of the most expansive rain forests in the world are in equatorial regions: the Amazon rain forest of South America, the Congo rain forest of Central Africa, and the varied Southeast Asian rainforest stretching from India to Vietnam.
Humid weather means that equatorial regions are not the hottest in the world, even though they are among the closest to the sun. The water in the equatorial air cools it slightly.
Many cultures thrive in warm equatorial regions. The Fang people of Gabon, for instance, are successful farmers who take advantage of the warm temperature and long rainy season to cultivate crops such as corn, yams, and plantains. The Fang also raise livestock that have adapted to the climate, such as goats and chickens.
Not all equatorial regions are hot and humid, however. Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania, is only 330 kilometers (205 miles) from the Equator, but its elevation creates a climate with cool, dry weather and even alpine glaciers.
The Andes are another equatorial region lacking the hot, humid climate often associated with the Equator. The mountain range includes a desert with almost no rain (the Atacama), as well as some of the tallest peaks on Earth. Here, too, cultures have thrived for thousands of years. The Aymara people of the Altiplano of Bolivia, Peru, and Chile, are primarily an urban people who identify strongly with the innovative navigational successes of their ancestors. In the 20th century, the Aymara helped build railroads through the high, equatorial Andes.
Many plant and animal species thrive in equatorial climates. The Amazon and Congo rain forest ecosystems, for example, are amazingly rich in biodiversity. A single hectare (2.47) of rain forest in Brazil may contain 750 species of trees and twice that many species of insects. The equatorial savanna of Kenya includes mammals such as lions, cheetahs, and elephants. The chilly equatorial Andes are famous for its camelid species: llamas, alpacas, vicunas, and guanacos.
FAST FACT
Bulging through Ecuador
Mount Chimborazo, Ecuadornot Mount Everestis the highest point on Earth. Earth's equatorial bulge pushes Mount Chimborazo, near the Equator in the Ecuadorian Andes, further from the center of the Earth.
However, elevation is measured from sea level, not the center of the Earth. Mount Everest is 8,848 meters (29,035 feet) above sea level, while Mount Chimborazo is just 6,310 meters (20,702 feet) above sea level.
FAST FACT
Crossing the Line
Sailors have elaborate rituals and celebrations when they cross the Equator, which they call crossing the line. Sailors who have never crossed the line are called pollywogs. Pollywogs are usually the target of embarrassing practical jokes.
FAST FACT
Short Sunsets
The time it takes for the sun to set and rise at the Equator is the fastest on Earth. The transition from day to night takes only a few minutes.