2.1 Basics of file
File
File सूचनाओं को संग्रहित करने का container है | यह characters की एक sequence (श्रंखला) है | यह सुचनाओं को संग्रहित करने की सबसे छोटी इकाई (smallest unit) है |
MS-DOS (Disk Operating System) की तरह UNIX file में EOF (End of File) का प्रयोग नहीं होता है |
File की size तथा इसके name को फाइल में संग्रहित नहीं किया जाता है |
फाइल attributes को एक separate area में रखा जाता है जिसे केवल kernel द्वारा ही access किया जा सकता है |
UNIX द्वारा directories तथा devices (hard disk/ printer/ memory/ CD-ROM/ modem) को भी file की तरह व्यक्त किया जाता है |
Shell and Kernel को भी फाइल में ही store किया जाता है |
प्रत्येक फाइल को उसके नाम तथा directory के नाम से जिसमें वह अवस्थित है, से identify किया जाता है | प्रत्येक फाइल का path होता है | path को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जाता है -
absolute path - path of the file with respect to root directory ( / )
relative path - path of the file with respect to any other directory
इसके अलावा प्रत्येक फाइल को एक unique number से identify किया जाता है जिसे inode number कहा जाता है |
UNIX File Types
- Ordinary Files – सामान्य फाइल –
यह वो file है जिसमें डाटा, text अथवा program instructions को store किया जाता है | text file, image file etc.
यह किसी डायरेक्टरी के अन्दर रहती है |
$ls –l command के output में इसके आगे “-” (hyphen) symbol प्रयुक्त होता है | इसमें अन्य file नहीं रहती है |
- Directory File –
यह special तथा ordinary (सामान्य) दोनों प्रकार की files को store करती है | इसे folder भी कहा जाता है |
directory file में इसमें store प्रत्येक file तथा sub-directory की entry रहती है |
प्रत्येक entry के दो अवयव होते है – i) Filename ii) file का unique id number (inode number) यह branching point को व्यक्त करता है | यह files के समूह को सुव्यवस्थित रखने में प्रयुक्त होता है | इसमें सामान्य file, special file तथा अन्य directory file रहती है | इसमें वास्तविक सुचना information नहीं रहती है |
$ls –l command के output में इसके आगे “d” symbol प्रयुक्त होता है |
- Special Files - इनका प्रयोग physical devices को व्यक्त करने के लिए होता है | जैसे – printer, CD-ROM, Tape-drive, या terminal (tty) ये devices Input/Output की क्रियाओं में प्रयुक्त होती है | device or special file का प्रयोग device I/O में होता होता है | ये devices file system में सामान्य file की तरह ही होती है | UNIX में दो तरह की special files होती है –
Character Special Files – data को byte-by-byte आदान-प्रदान (Read/ Write) किया जाता है| इसे raw device access कहा जाता है | $ls –l command में इन files के लिए “c” symbol प्रयुक्त होता है |
Block Special Files – data का आदान-प्रदान large fixed-size block में किया जाता है | इसे block device access कहा जाता है | $ls –l command में इन files के लिए “b” प्रयुक्त होता है |
- Pipes – UNIX में pipe ( | ) द्वारा commands को आपस में लिंक किया जा सकता है | Pipe एक विशेष प्रकार की temporary file है जो एक command का data दुसरे command तक भेजने का काम करती है | दुसरे command को data भेजने के बाद इसका कोई अस्तित्व नहीं रहता है| यह केवल एक ही दिशा में data के प्रवाह को support करता है | पहले command का output दुसरे command के लिए input होता है | Pipe को vertical bar से व्यक्त किया जाता है |
$ls –l के output में pipe files के लिए “p” symbol प्रयुक्त होता है |
- Sockets – यह एक विशेष file है जो inter-process communication में प्रयुक्त होती है | इसका प्रयोग client-server applications में होता है |
$ls –l command के output में Socket file के लिए “s” symbol का प्रयोग होता है |
- Symbolic Link – यह किसी file का reference है | इसे soft link भी कहा जाता है | यदि हम source file को delete कर दे या हटा दे तो symbolic link काम नहीं करेगा |
$ls –l command के output में Symbolic link के लिए “l” (small L) प्रयुक्त होता है |
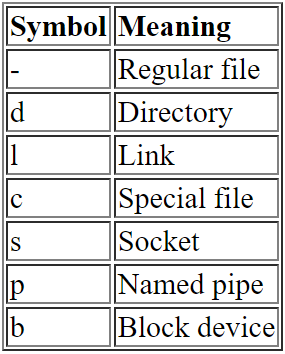
Fig. 2.1.1 UNIX File Types